Powerful complex for children’s immune system!
Code:
4751018781851
Packaging:
10 Sachets

Powerful complex for children’s immune system, based on strong immunomodulatory ingredient yeast beta glucan in combination with essential vitamins and minerals, that effectively reduces the incidence and duration of common cold.

Children are more prone to the viruses, than adults, because of having an immature immune system.
While we can’t control every cold, that comes along, we can help decrease the incidence and duration of common cold and build strong immune system in simple way.


Yeast beta glucan is scientifically proven to be a strongest ingredient for the immune system protection.
Children taking yeast beta glucan had two-thirds fewer upper respiratory tract infections (URTI) and six fewer sick days period compared to placebo.


Vitamins and minerals play important roles in supporting the immune system and their deficiencies could increase the susceptibility of child to infectious diseases.
Adequate levels of micronutrients are essential to ensure an effective function of each component of the immune system.
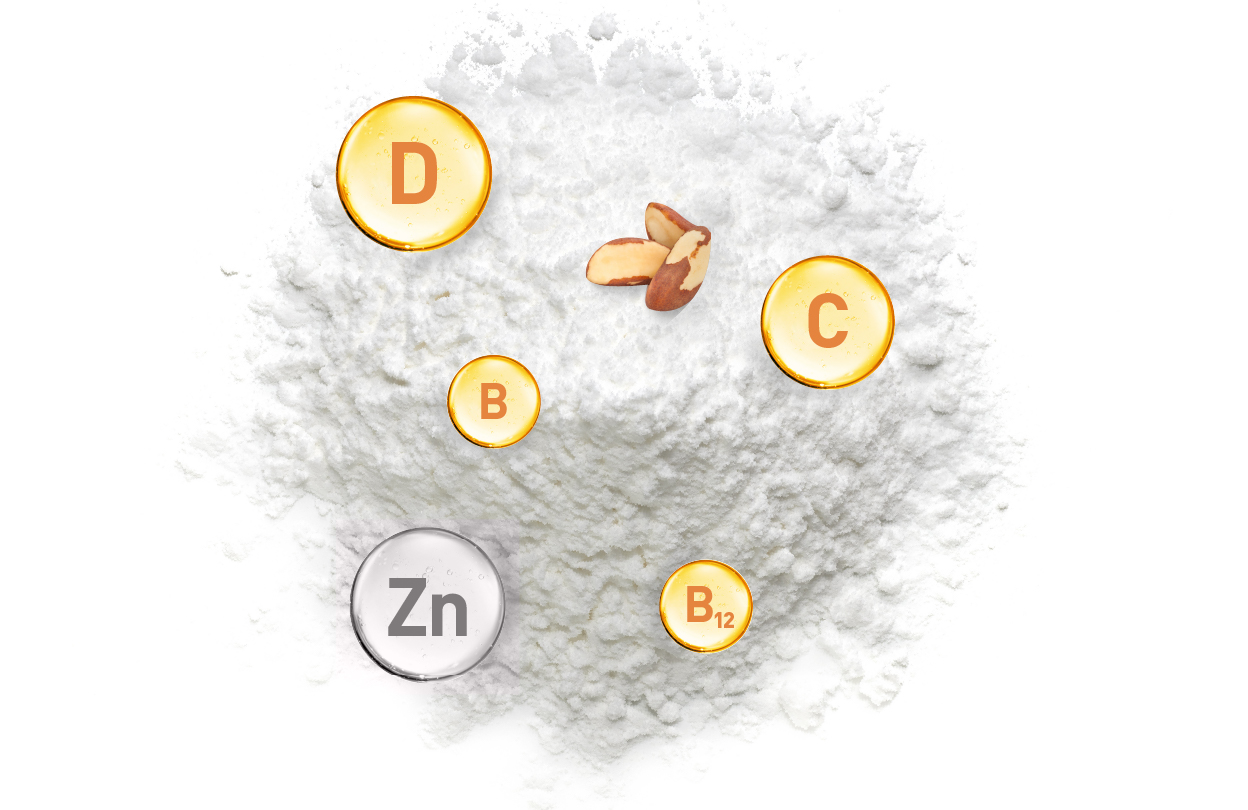

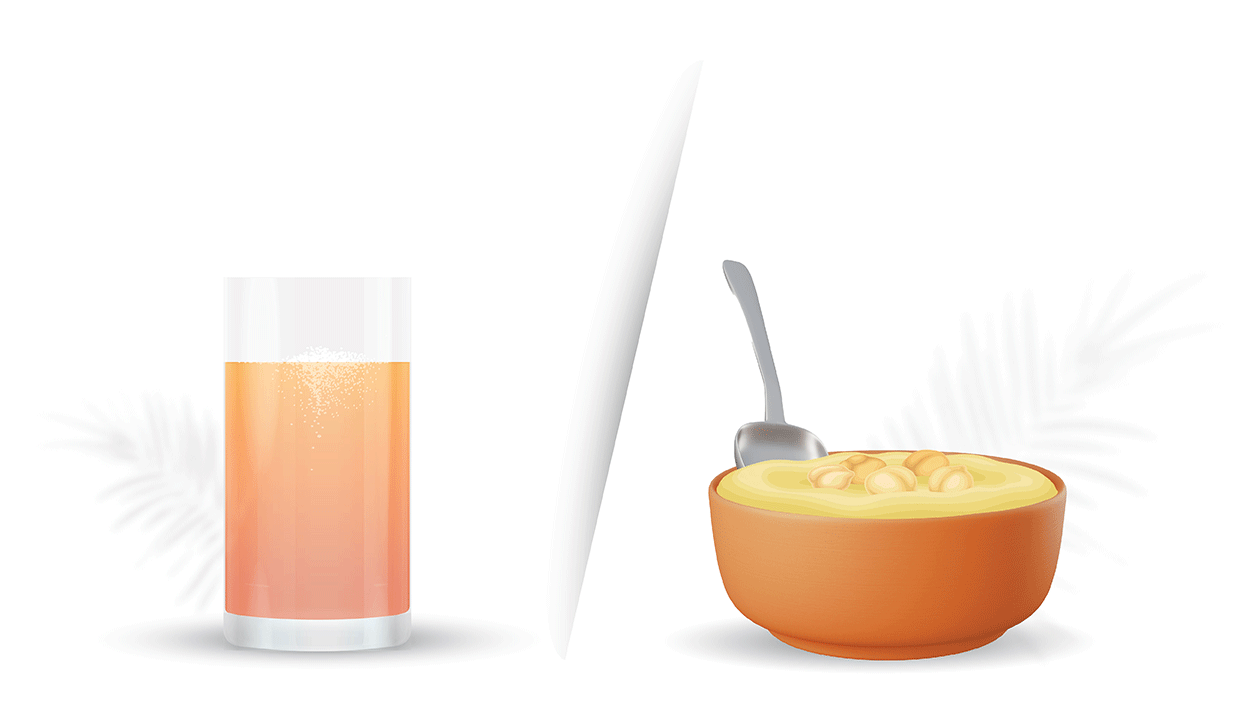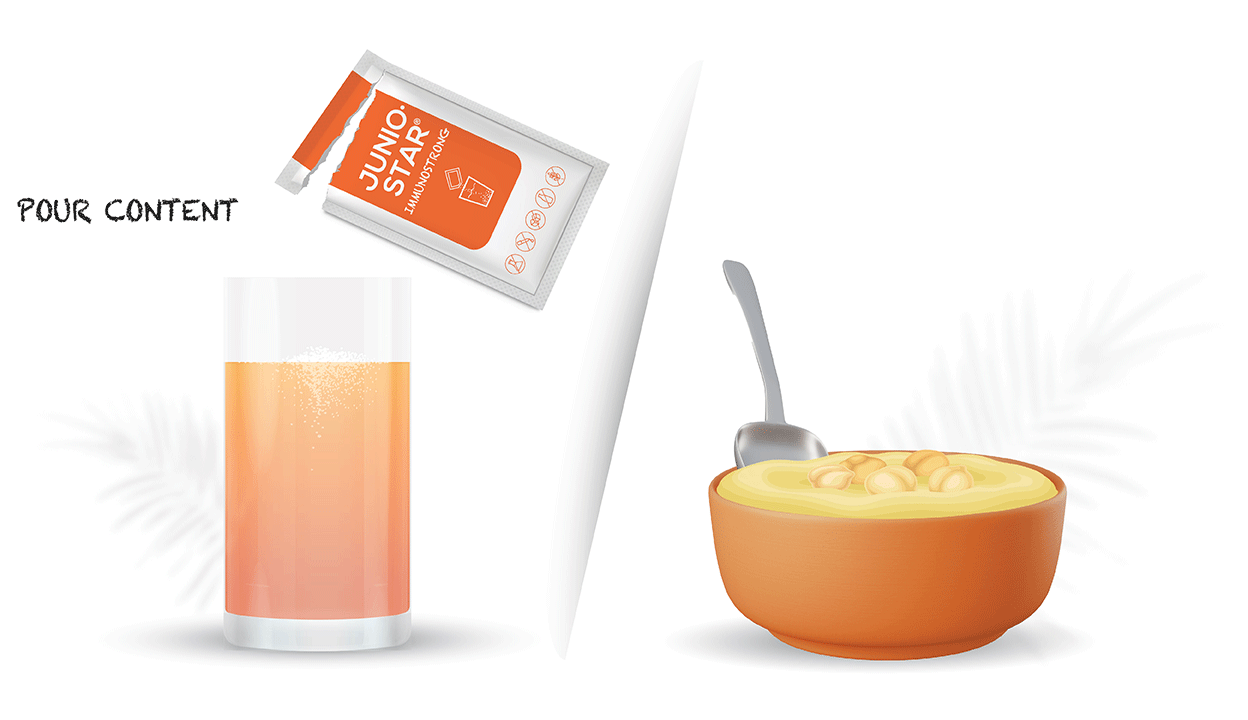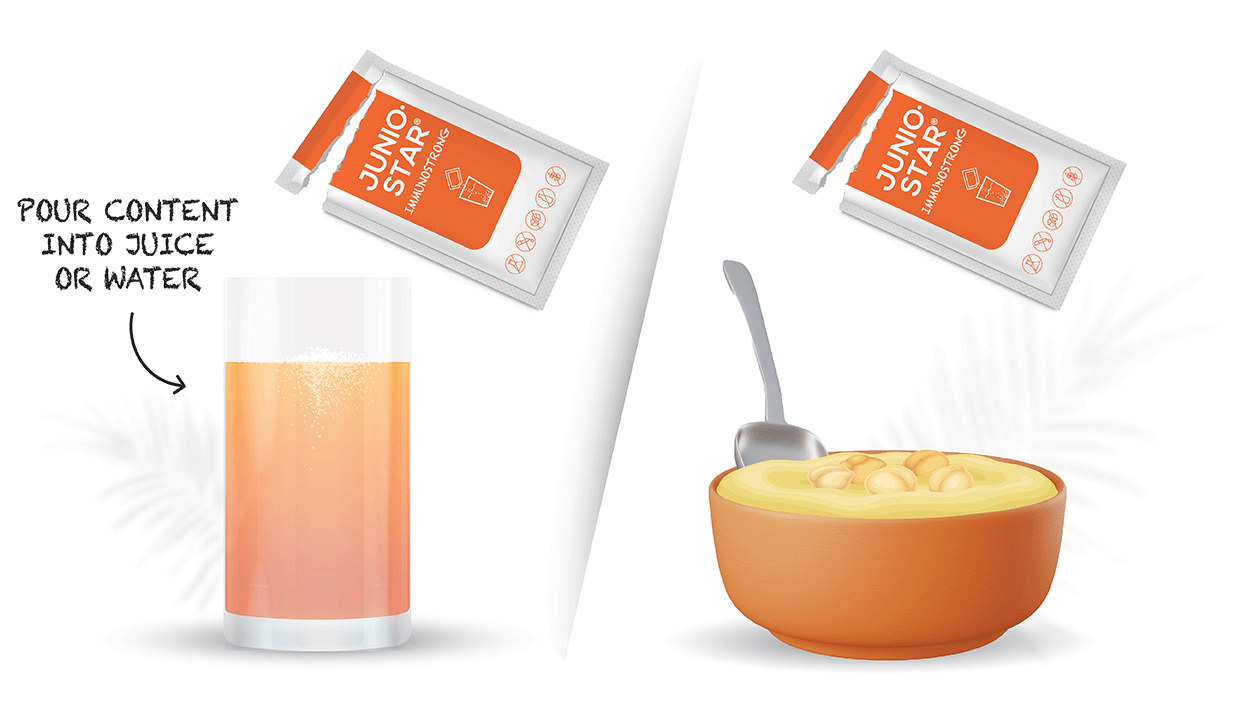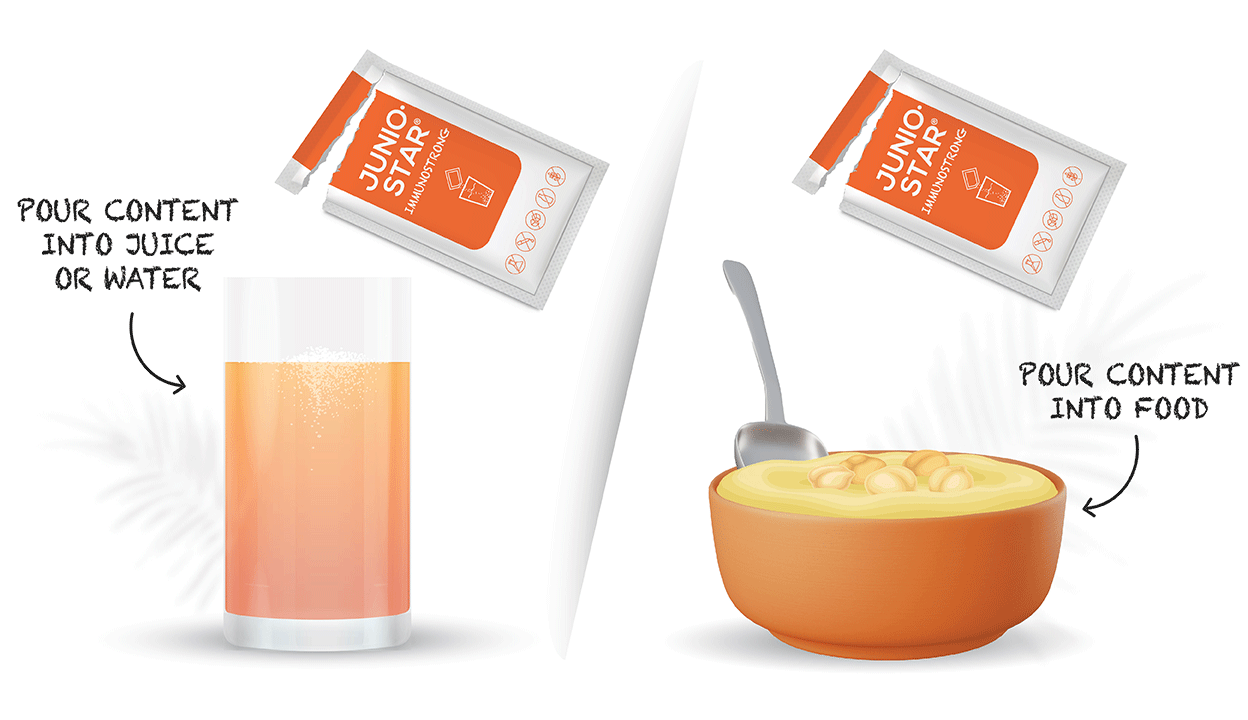
Usage: recommended for children from the age of 1 – 6 to use internally 1 sachet once per day after the meal, for children from the age of 7 – 12 – 1 sachet twice per day after the meal. Dilute the content of sachet in the glass of water or juice or meal in room temperature. Duration of usage up to 6 months. Warnings: do not use food supplement as the substitute of balanced and valuable nutrition; do not exceed recommended daily dosage; high sensitivity (allergy) towards some of the product ingredients; keep out of reach and sight of children! Store at room temperature in original packaging avoiding direct sunlight.

STUDY
The aim of the study was to evaluate the ability of yeast beta glucan to reduce the number of episodes of common childhood illness in children from 1 to 4 years old.
RESULTS
Study has shown absorption from chelated iron to be 4 times higher than other iron forms1. Study showed that children in yeast beta glucan group experienced less common childhood infectious illness episodes compared to the placebo group and were well tolerated for the children from 1 to 4 years old1.
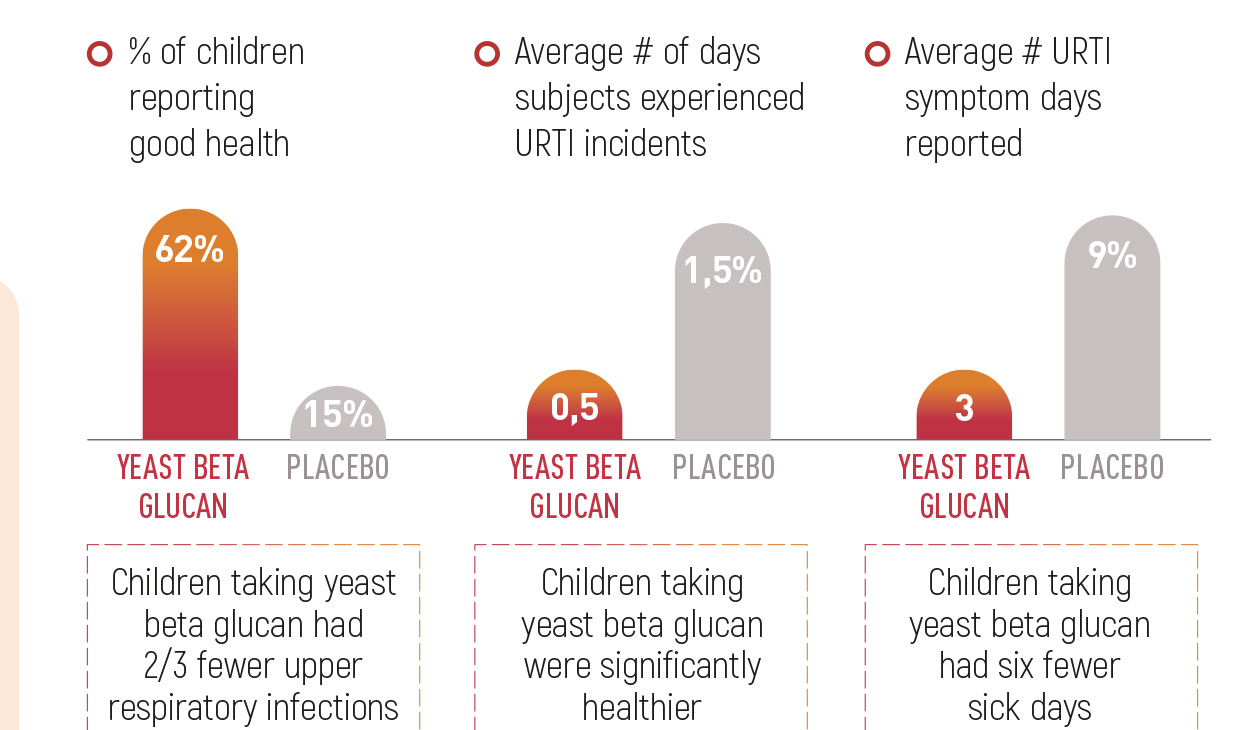
F, Meng. (2016). Bakers Yeast Beta-Glucan Decreases Episodes of Common Childhood Illness in 1 to 4 Year Old Children during Cold Season in China. Journal of Nutrition & Food Sciences. 6. 10.4172/2155-9600.1000519.
STUDY
The aim fo the study was to evaluate the effect of vitamin C in preventing and relieving cold and flu symptoms.
RESULTS
Study showed, that overall, reported flu and cold symptoms in the test group decreased by 85% compared with the control group after the administration of vitamin C.
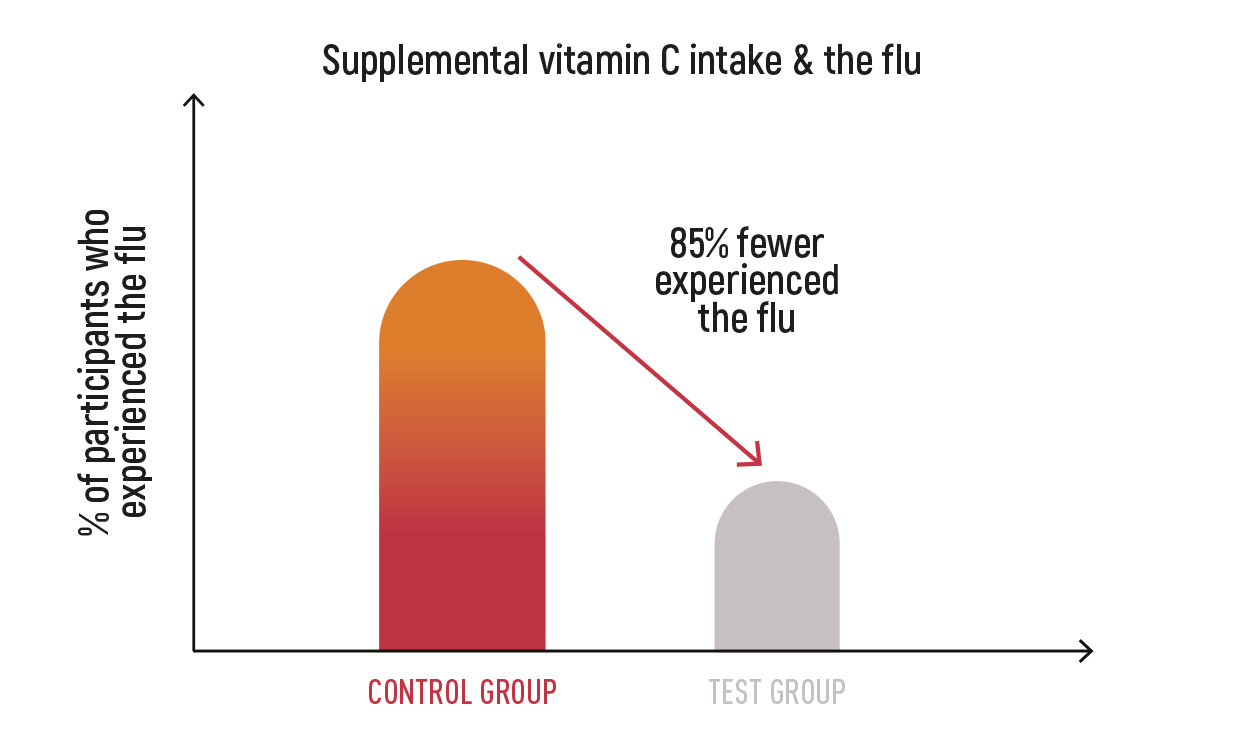
Gorton, H C, and K Jarvis. “The effectiveness of vitamin C in preventing and relieving the symptoms of virus-induced respiratory infections.” Journal of manipulative and physiological therapeutics vol. 22,8 (1999): 530-3.
STUDY
The aim of the study was to explore the usefulness of early micronutrient intervention, with focus on zinc, selenium, and vitamin D, to relieve escalation of COVID-19.
RESULTS
Study provided direct evidence on associations between zinc, selenium, and vitamin D, and COVID-19. Adequate supply of zinc, selenium, and vitamin D is essential for resistance to other viral infections, immune function, and reduced inflammation.
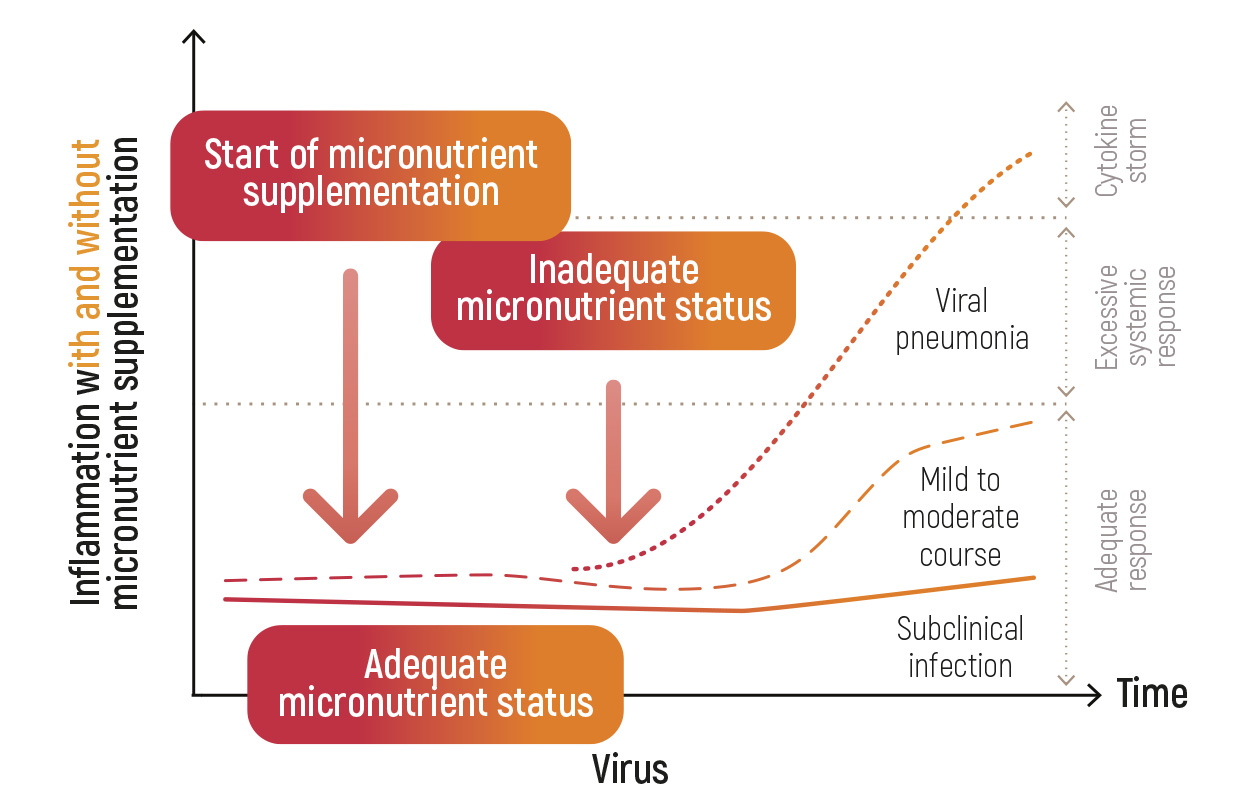
Alexander, Jan et al. “Early Nutritional Interventions with Zinc, Selenium and Vitamin D for Raising Anti-Viral Resistance Against Progressive COVID-19.” Nutrientsvol. 12,8 2358. 7 Aug. 2020.
STUDY
The study was performed to assess whether L-arginine supplementation could improve the outcomes of immune function.
RESULTS
Study showed that the L-arginine supplement group had a significantly greater CD4+ T-cell proliferation response (MD 5.03; 95% CI 1.11, 8.95; p<0.05), and that the incidence of infectious complications was lower (OR 0.40; 95% CI 0.17, 0.95; p<0.05) than control.
Kang, Kai et al. “Effect of L-arginine on immune function: a meta-analysis.” Asia Pacific journal of clinical nutrition vol. 23,3 (2014): 351-9.
STUDY
The study was performed to assess whether vitamin B deficiency can significantly impair cell and immune system function, and lead to inflammation due to hyperhomocysteinemia.
RESULTS
Study showed, that vitamin B modulates immune response by downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines and inflammation, reducing breathing difficulty and gastrointestinal problems, preventing hypercoagulability, potentially improving outcomes and reducing the length of stay in the hospital for COVID-19 patients.
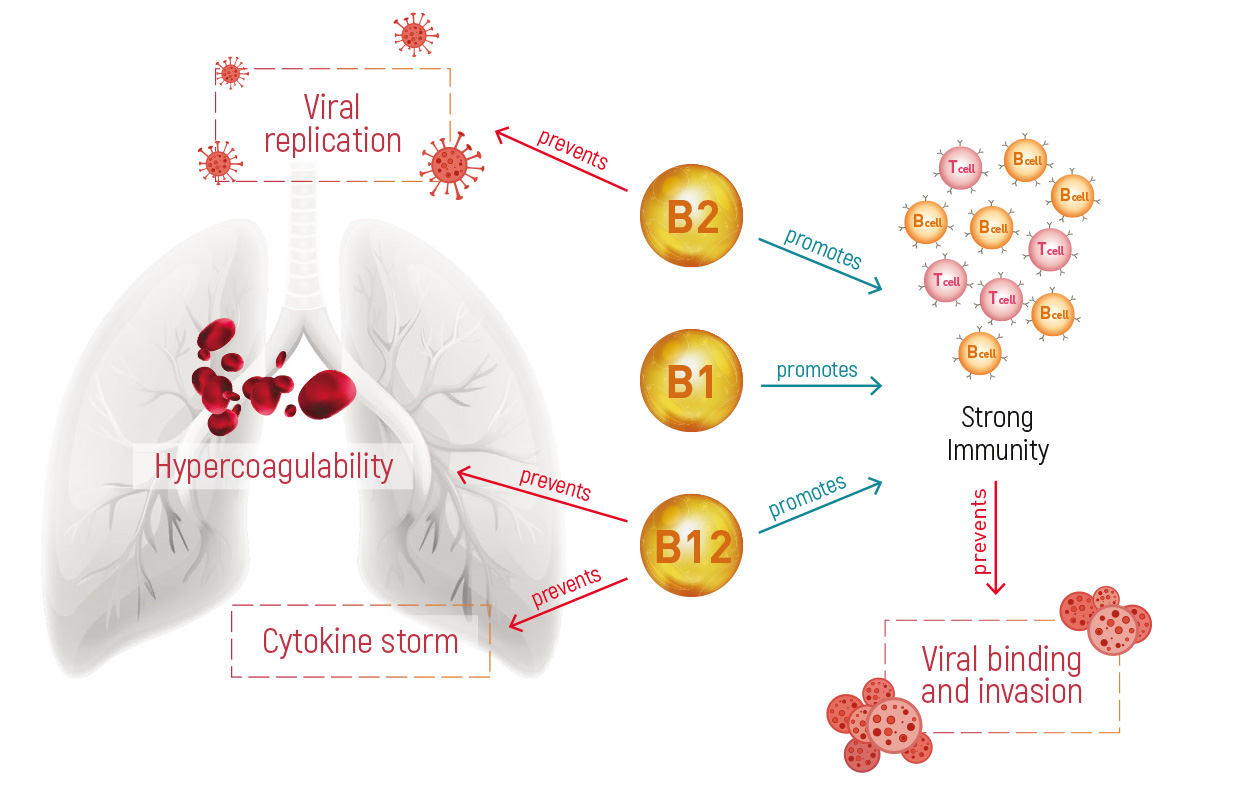
Shakoor, Hira et al. “Be well: A potential role for vitamin B in COVID-19.” Maturitas vol. 144 (2021): 108-11
National Organization for Medicines (EOF) of Greece (EOF Notification No.: 41010/24-04-2023),GMP
Usage: recommended for children from the age of 1 – 6 to use internally 1 sachet once per day after the meal, for children from the age of 7 – 12 – 1 sachet twice per day after the meal. Dilute the content of sachet in the glass of water or juice or meal in room temperature. Duration of usage up to 6 months. Warnings: do not use food supplement as the substitute of balanced and valuable nutrition; do not exceed recommended daily dosage; high sensitivity (allergy) towards some of the product ingredients; keep out of reach and sight of children! Store at room temperature in original packaging avoiding direct sunlight.

STUDY
The aim of the study was to evaluate the ability of yeast beta glucan to reduce the number of episodes of common childhood illness in children from 1 to 4 years old.
RESULTS
Study has shown absorption from chelated iron to be 4 times higher than other iron forms1. Study showed that children in yeast beta glucan group experienced less common childhood infectious illness episodes compared to the placebo group and were well tolerated for the children from 1 to 4 years old1.

F, Meng. (2016). Bakers Yeast Beta-Glucan Decreases Episodes of Common Childhood Illness in 1 to 4 Year Old Children during Cold Season in China. Journal of Nutrition & Food Sciences. 6. 10.4172/2155-9600.1000519.
STUDY
The aim fo the study was to evaluate the effect of vitamin C in preventing and relieving cold and flu symptoms.
RESULTS
Study showed, that overall, reported flu and cold symptoms in the test group decreased by 85% compared with the control group after the administration of vitamin C.

Gorton, H C, and K Jarvis. “The effectiveness of vitamin C in preventing and relieving the symptoms of virus-induced respiratory infections.” Journal of manipulative and physiological therapeutics vol. 22,8 (1999): 530-3.
STUDY
The aim of the study was to explore the usefulness of early micronutrient intervention, with focus on zinc, selenium, and vitamin D, to relieve escalation of COVID-19.
RESULTS
Study provided direct evidence on associations between zinc, selenium, and vitamin D, and COVID-19. Adequate supply of zinc, selenium, and vitamin D is essential for resistance to other viral infections, immune function, and reduced inflammation.

Alexander, Jan et al. “Early Nutritional Interventions with Zinc, Selenium and Vitamin D for Raising Anti-Viral Resistance Against Progressive COVID-19.” Nutrientsvol. 12,8 2358. 7 Aug. 2020.
STUDY
The study was performed to assess whether L-arginine supplementation could improve the outcomes of immune function.
RESULTS
Study showed that the L-arginine supplement group had a significantly greater CD4+ T-cell proliferation response (MD 5.03; 95% CI 1.11, 8.95; p<0.05), and that the incidence of infectious complications was lower (OR 0.40; 95% CI 0.17, 0.95; p<0.05) than control.

Kang, Kai et al. “Effect of L-arginine on immune function: a meta-analysis.” Asia Pacific journal of clinical nutrition vol. 23,3 (2014): 351-9.
STUDY
The study was performed to assess whether vitamin B deficiency can significantly impair cell and immune system function, and lead to inflammation due to hyperhomocysteinemia.
RESULTS
Study showed, that vitamin B modulates immune response by downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines and inflammation, reducing breathing difficulty and gastrointestinal problems, preventing hypercoagulability, potentially improving outcomes and reducing the length of stay in the hospital for COVID-19 patients.

Shakoor, Hira et al. “Be well: A potential role for vitamin B in COVID-19.” Maturitas vol. 144 (2021): 108-11
National Organization for Medicines (EOF) of Greece (EOF Notification No.: 41010/24-04-2023),GMP